| Menu: | Analysis→Contiguous Data→QuadVar→Quadrat Variance Methods |
| Button: | |
| Batch: | QuadVar |
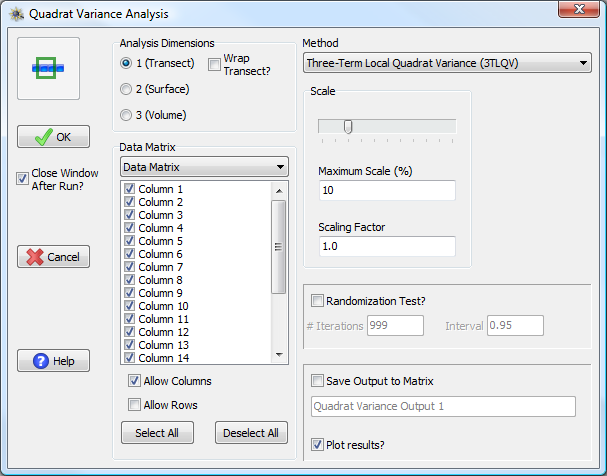
Quadrat Variance Methods window
To run a quadrat variance analysis in PASSaGE, one must first specify the dimensionality of the analysis they wish to run. The specific methods available in the drop down box in the upper right will vary depending on the dimensionality of the analysis. One dimensional analyses have an additional option known as Wrap Transect? If this box is checked, PASSaGE will assume that the ends of the transect meet in a circle and calculations are adjusted to account for the adjacency of the endpoints. This option should be used for circular data with arbitrary endpoints (e.g., an analysis of data from a circular chromosome).
One must also specify a data matrix from which to extract data for the analysis and the specific data to extract. The specific options depend on the dimensionality of both the analysis and the input data. PASSaGE allows one to perform quadrat variance analysis on multiple data sets simultaneously by choosing multiple columns (and/or rows or surfaces) from a single input matrix.
Quadrat variance analysis is performed for all scales (block sizes) from one to a maximum specified as a percentage of the input data size. The maximum allowable scale varies by method. Generally, two-term methods allow analysis up to 50% of the data length and three-term methods allow analysis up to 33% of the data length. Other methods may have tighter restrictions depending on the shape of the method's template.
Randomization tests for quadrat variance analysis work by randomizing the order of the quadrats within the transect (or surface or volume) and recalculating the variance profile for the randomized data. This generates a null distribution of expected variances for data with the specific observed values but with no specific geographic relationships. Significant scales of clustering can be identified from the observed data when the observed peak exceeds the expectation generated from the randomization test. Quadrat Variance analysis is essentially one-tailed.